The most forward-looking small businesses find smarter ways to stay lean and agile. Right now, oneof the best strategies is business process outsourcing (BPO). In short, it’s a way for businesses to hand off certain business operations to an external service provider – freeing up time and resources to focus on their own business growth.
While BPO may sound like a solution only large corporations would pursue, the reality is that the outsourcing industry is increasingly servicing small businesses, too. From outsourcing customer service and payroll to leveraging specialised services like legal research or market analytics, the right BPO provider can cut down your costs and supercharge your competitive edge.
Here’s how BPO works and why it might make good sense for your business.
BPO meaning and definition
Business process outsourcing is the practice of contracting out business functions to a third-party service provider. Business process outsourcing services typically encompass non-core business functions, such as payroll, accounting, human resources management, customer support, and IT services. That being said, some companies also outsource higher-value services like legal or research functions.
There are three common types of BPO based on provider location:
- Onshore outsourcing (domestic outsourcing): The BPO company is from the same country as the hiring company.
- Nearshore outsourcing: The service provider is in a neighbouring or nearby country.
- Offshore outsourcing: The service provider is located in a different country, typically chosen due to lower costs or 24/7 availability.
The business process outsourcing industry began in the manufacturing industry, where businesses outsourced parts of their supply chain to third-party vendors. Today, BPO services span nearly every sector – from healthcare and legal to finance, e-commerce and real estate.
Why do businesses outsource processes?
Small businesses usually don’t have the in-house resources to manage every business function themselves. Outsourcing services means they can take advantage of specialised expertise without hiring full-time staff. Things like outsourcing payroll or payment processing, for example, can simplify your internal business functions, while outsourcing customer service can help create a better customer experience without hiring a full support team.
Larger businesses can also turn to BPO providers to keep their operating costs down or expand internationally – without the need for massive infrastructure investments.
What types of business functions are commonly outsourced?
Organisations of all sizes and industry types can outsource their business processes across both their front-office and back-office functions.
Back-office functions (supporting operations) include:
- Accounting and bookkeeping.
- IT management.
- Payment processing.
- Human resources and recruitment.
- Supply chain management.
Whereas front-office functions (customer-facing) cover things like:
- Phone support and email/chat support.
- Marketing services.
- Customer service processes.
- Market research and analytics.
Some companies choose to outsource an entire function (like HR), while others only outsource specific tasks (like payroll or candidate screening).
Types of BPO services
Beyond general outsourcing, the BPO market includes more specialised subsets that can handle knowledge-based tasks:
- Knowledge process outsourcing (KPO): Outsourcing services that involve specific knowledge sets or analytical expertise – think data mining, financial forecasting, strategic market research, etc.
- Legal process outsourcing (LPO): Contracting legal services like contract drafting, compliance checks or legal research to external providers.
- Research process outsourcing (RPO): Delegating research and analysis functions to external experts. This tends to be used in investment, healthcare, marketing and biotechnology.
Other growing areas include IT-enabled services (ITES), which manage digital operations like software development or data entry, as well as recruitment process outsourcing, which externalises hiring functions.
How does business process outsourcing work?
Generally, business process outsourcing follows these steps:
- Identify non-core functions that can be outsourced.
- Define your goals and expectations (e.g. cost savings, improved performance, business automation).
- Compare potential BPO vendors in terms of their industry knowledge, technical capabilities, cost structure and service-level commitments.
- Create a BPO contract that outlines the scope, pricing (e.g. time and materials or fixed-price), service levels and key performance indicators (KPIs).
- Transition the process from your in-house team to the BPO company – this includes onboarding, knowledge transfer, systems integration and more.
As with any major operational shift, change management is central to success (or failure). Successful BPO collaborations will depend on whether there’s alignment among internal stakeholders and as little disruption as possible.
Benefits of BPO for small businesses
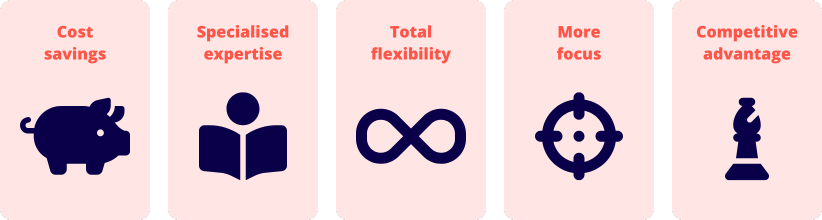
BPO has some major pros for small businesses:
- Cost savings: Cheaper labour and operational costs are arguably the biggest drivers of BPO adoption – especially true for offshore outsourcing, where wages and overheads are lower.
- Specialised expertise: A BPO company brings skills and technology that a small in-house team might not have.
- Total flexibility: Businesses can scale their services up or down quickly based on market demand without committing to long-term overheads.
- More focus: Outsourcing non-core business functions means your team can redirect their attention to core business growth.
- Competitive advantage: Leveraging the right BPO providers can translate to higher-quality work, faster turnaround times and innovation from technologies like robotic process automation.
Risks to consider

While there are some major benefits to business process outsourcing, it also carries its own set of risks that you’ll need to be prepared for:
- Data security concerns: Sharing sensitive information with a third party can expose your business to cyber threats or compliance problems.
- Hidden costs or scope creep: Without well-defined contracts, you could see your BPO costs skyrocket over time.
- Loss of control or quality: Relying too heavily on an external service provider can make it harder to maintain your quality levels or pivot at a moment’s notice.
- Reputational risks: Poor customer service from an outsourced team could damage your customer relationships or even your brand reputation.
For these reasons, you’ll need to take enough time to pick the right BPO company for your needs. You’ll also need to stay on top of all potential issues with robust contracts and reporting metrics.
How to choose the right BPO provider
Finding the right BPO partner should start with you looking for proven experience in your industry or with similar businesses. You’ll want them to be able to demonstrate their understanding of your business operations and goals, and that they have a solid approach to data privacy and legal frameworks.
Once you get into the nitty-gritty, you’ll want transparent service-level agreements and KPI tracking, as well as the flexibility to adapt and scale their services as your business grows.
A knowledge management system or internal knowledge base can also help onboard BPO providers, giving them the context and documentation they need to operate without disruption.
Business process outsourcing can be a great tool for startups and growing businesses alike. But if you’ve never used a BPO provider before, make sure to start small. Outsource your non-core business functions and partner with providers who understand your overarching business goals.
See related terms
What is capital expenditure (CapEx)?
What is a Key Performance Indicator?
What is an operating expense?